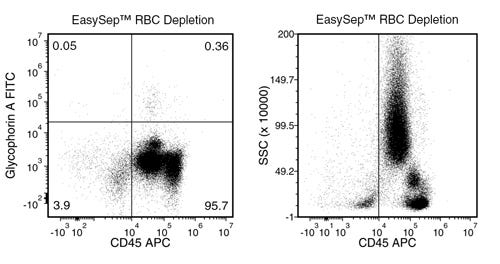
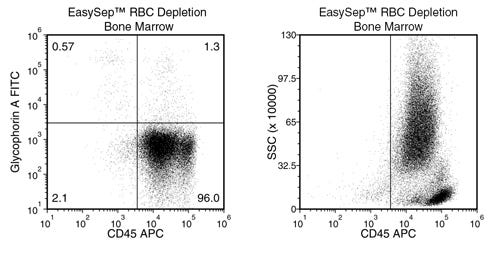
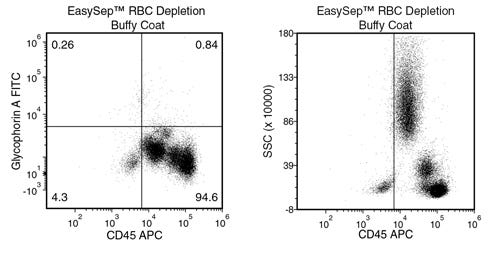
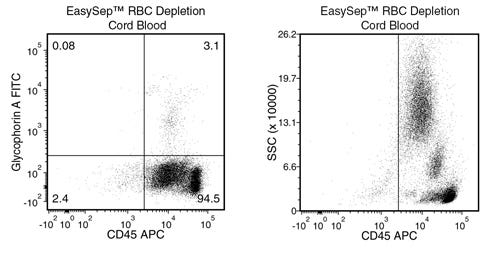
EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent
Immunomagnetic depletion of RBCs
New look, same high quality and support! You may notice that your instrument or reagent packaging looks slightly different from images displayed on the website, or from previous orders. We are updating our look but rest assured, the products themselves and how you should use them have not changed. Learn more
Overview
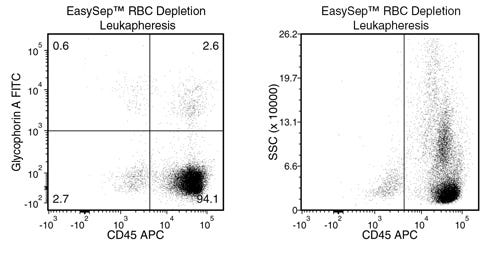
Data Figures
Protocols and Documentation
Find supporting information and directions for use in the Product Information Sheet or explore additional protocols below.
Applications
This product is designed for use in the following research area(s) as part of the highlighted workflow stage(s). Explore these workflows to learn more about the other products we offer to support each research area.
Resources and Publications
Educational Materials (15)
Publications (3)
Single-cell analysis of menstrual endometrial tissues defines phenotypes associated with endometriosis.
BMC medicine 2022 sep
Abstract
BACKGROUND Endometriosis is a common, complex disorder which is underrecognized and subject to prolonged delays in diagnosis. It is accompanied by significant changes in the eutopic endometrial lining. METHODS We have undertaken the first single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-Seq) comparison of endometrial tissues in freshly collected menstrual effluent (ME) from 33 subjects, including confirmed endometriosis patients (cases) and controls as well as symptomatic subjects (who have chronic symptoms suggestive of endometriosis but have not been diagnosed). RESULTS We identify a unique subcluster of proliferating uterine natural killer (uNK) cells in ME-tissues from controls that is almost absent from endometriosis cases, along with a striking reduction of total uNK cells in the ME of cases (p??<??10-16). In addition, an IGFBP1+ decidualized subset of endometrial stromal cells are abundant in the shed endometrium of controls when compared to cases (p??<??10-16) confirming findings of compromised decidualization of cultured stromal cells from cases. By contrast, endometrial stromal cells from cases are enriched in cells expressing pro-inflammatory and senescent phenotypes. An enrichment of B cells in the cases (p??=??5.8???—??10-6) raises the possibility that some may have chronic endometritis, a disorder which predisposes to endometriosis. CONCLUSIONS We propose that characterization of endometrial tissues in ME will provide an effective screening tool for identifying endometriosis in patients with chronic symptoms suggestive of this disorder. This constitutes a major advance, since delayed diagnosis for many years is a major clinical problem in the evaluation of these patients. Comprehensive analysis of ME is expected to lead to new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to endometriosis and other associated reproductive disorders such as female infertility.
Single-cell immunophenotyping of the fetal immune response to maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection in late gestation.
Pediatric research 2022 apr
Abstract
BACKGROUND During the COVID-19 pandemic, thousands of pregnant women have been infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The implications of maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection on fetal and childhood well-being need to be characterized. We aimed to characterize the fetal immune response to maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection. METHODS We performed single-cell RNA-sequencing and T cell receptor sequencing on cord blood mononuclear cells (CBMCs) from newborns of mothers infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the third trimester (cases) or without SARS-CoV-2 infection (controls). RESULTS We identified widespread gene expression changes in CBMCs from cases, including upregulation of interferon-stimulated genes and major histocompatibility complex genes in CD14+ monocytes, transcriptional changes suggestive of activation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells, and activation and exhaustion of natural killer cells. Lastly, we observed fetal T cell clonal expansion in cases compared to controls. CONCLUSIONS As none of the infants were infected with SARS-CoV-2, our results suggest that maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection might modulate the fetal immune system in the absence of vertical transmission. IMPACT The implications of maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection in the absence of vertical transmission on fetal and childhood well-being are poorly understood. Maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection might modulate the fetal immune system in the absence of vertical transmission. This study raises important questions about the untoward effects of maternal SARS-CoV-2 on the fetus, even in the absence of vertical transmission.
Dissecting the mechanism of cytokine release induced by T-cell engagers highlights the contribution of neutrophils.
Oncoimmunology 2022
Abstract
T cell engagers represent a novel promising class of cancer-immunotherapies redirecting T cells to tumor cells and have some promising outcomes in the clinic. These molecules can be associated with a mode-of-action related risk of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in patients. CRS is characterized by the rapid release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-$\alpha$, IFN-$\gamma$, IL-6 and IL-1$\beta$ and immune cell activation eliciting clinical symptoms of fever, hypoxia and hypotension. In this work, we investigated the biological mechanisms triggering and amplifying cytokine release after treatment with T cell bispecific antibodies (TCBs) employing an in vitro co-culture assay of human PBMCs or total leukocytes (PBMCs + neutrophils) and corresponding target antigen-expressing cells with four different TCBs. We identified T cells as the triggers of the TCB-mediated cytokine cascade and monocytes and neutrophils as downstream amplifier cells. Furthermore, we assessed the chronology of events by neutralization of T-cell derived cytokines. For the first time, we demonstrate the contribution of neutrophils to TCB-mediated cytokine release and confirm these findings by single-cell RNA sequencing of human whole blood incubated with a B-cell depleting TCB. This work could contribute to the construction of mechanistic models of cytokine release and definition of more specific molecular and cellular biomarkers of CRS in the context of treatment with T-cell engagers. In addition, it provides insight for the elaboration of prophylactic mitigation strategies that can reduce the occurrence of CRS and increase the therapeutic index of TCBs.
New look, same high quality and support! You may notice that your instrument or reagent packaging looks slightly different from images displayed on the website, or from previous orders. We are updating our look but rest assured, the products themselves and how you should use them have not changed. Learn more
Quality Statement:
PRODUCTS ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USES UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON QUALITY AT STEMCELL, REFER TO WWW.STEMCELL.COM/COMPLIANCE.
PRODUCTS ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY AND NOT INTENDED FOR HUMAN OR ANIMAL DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USES UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED. FOR ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ON QUALITY AT STEMCELL, REFER TO WWW.STEMCELL.COM/COMPLIANCE.