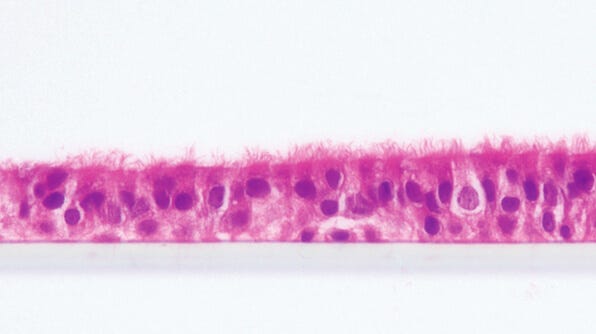
Modeling Cystic Fibrosis Airway
Introduction
Cystic Fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that impacts 70,000 people worldwide.1 It is caused by mutations in the gene encoding the CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), a chloride channel on the apical surface of the epithelium, leading to aberrant ion transport and mucus buildup in the lungs, pancreas, and other organs.2 Impaired mucociliary clearance in the airway results in chronic infection, inflammation, tissue damage, and respiratory failure.
Innovative therapeutics have been developed using animal models and in vitro cultures to target specific mutations in the CFTR gene.2 Air-liquid interface (ALI) cultures of primary human airway epithelial cells are well-adopted in the CF research field, although different research groups tend to prefer different media formulations.3,4,5 One of the media formulations containing Ultroser® G, a type of serum substitute, was found to be predictive of clinical outcomes for FDA-approved therapeutics.6,7 However, given that access to this proprietary component can be unreliable, CF researchers are testing alternative cell culture media that can generate physiologically relevant, electrophysiological readouts.8
Why Use PneumaCult™ for CF Research?
PneumaCult™ media products are serum- and bovine pituitary extract (BPE)-free, specifically designed for the robust expansion and ALI differentiation of primary human airway epithelial cells. A side-by-side comparison has been made between various expansion and ALI differentiation media from early to late passages using CF airway epithelial cells. Optimal culture morphology and electrophysiological characteristics are obtained using PneumaCult™-Ex Plus for expansion followed by PneumaCult™-ALI for differentiation, especially after extended passaging.
- Physiologically relevant proportion of different cell types.
- More cells at each passage.
- Maintained morphological and electrophysiological
characteristics, even after extended passaging. - Serum- and BPE-free to reduce lot-to-lot variability.
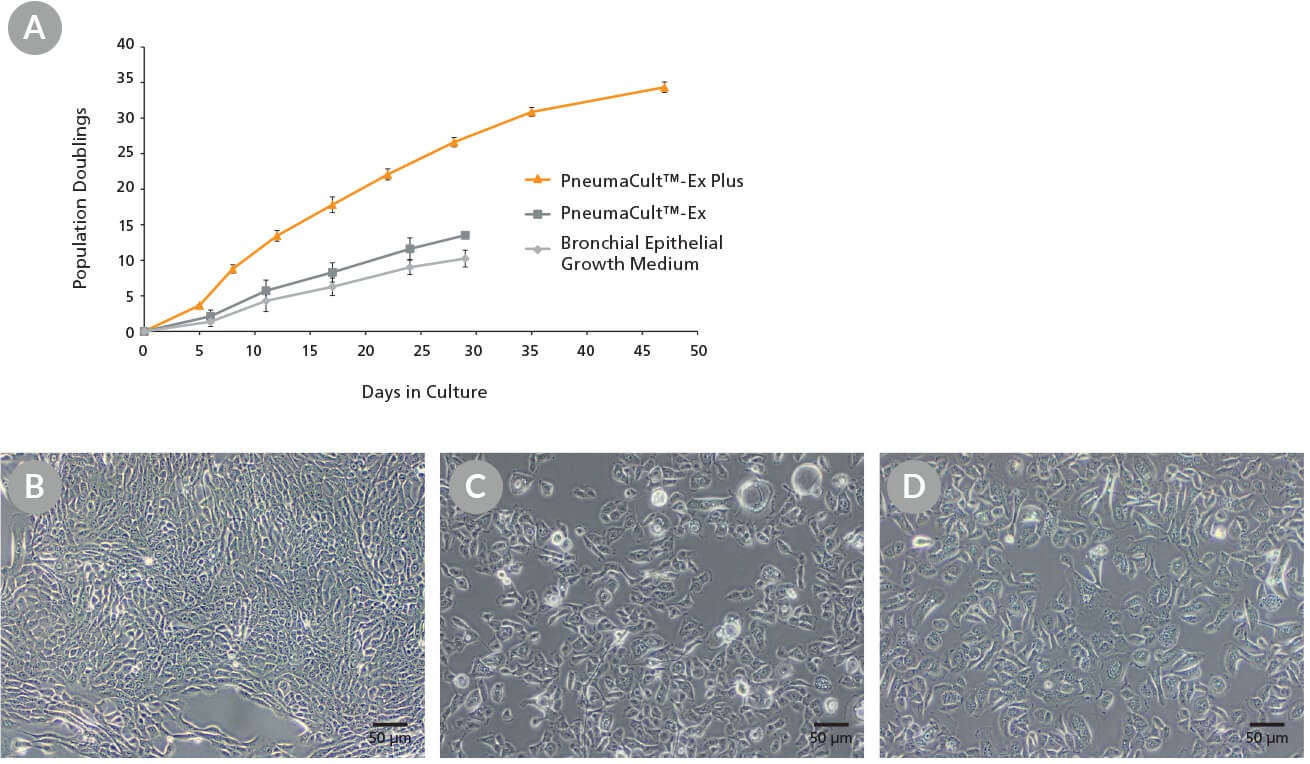
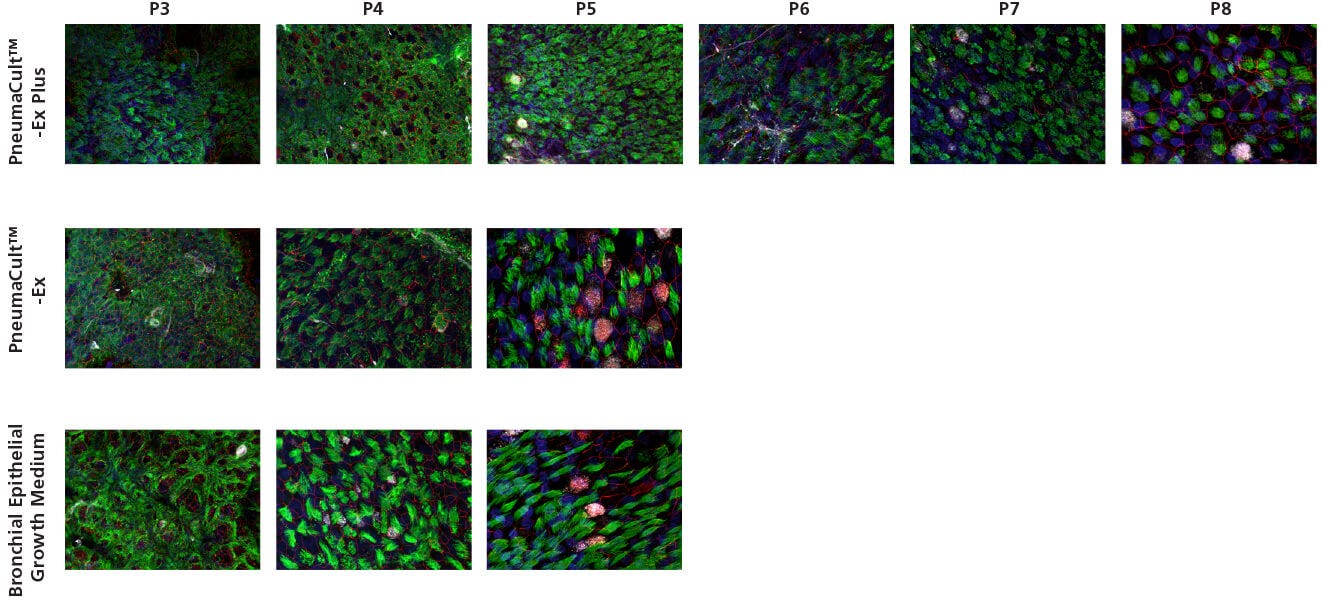
Figure 1. Growth and Morphology of CF HBECs During Expansion
Commercially-available, cryopreserved P2 CF human bronchial epithelial cells (HBECs) were seeded into PneumaCult™-Ex Plus, PneumaCult™-Ex, or Bronchial Epithelial Growth Medium. (A) Cells cultured in PneumaCult™-Ex Plus exhibit significantly higher proliferation rate over 8 passages compared to those maintained in either control medium (n = 3). Cell cultures using PneumaCult™-Ex or Bronchial Epithelial Growth Medium were terminated at P5 due to declining differentiation potential. (B-D) Representative morphology of P4 CF HBECs expanded in (B) PneumaCult™-Ex Plus, (C) PneumaCult™-Ex, or (D) Bronchial Epithelial Growth Medium.
PneumaCult™-ALI
Ultroser® G-Based Formulation
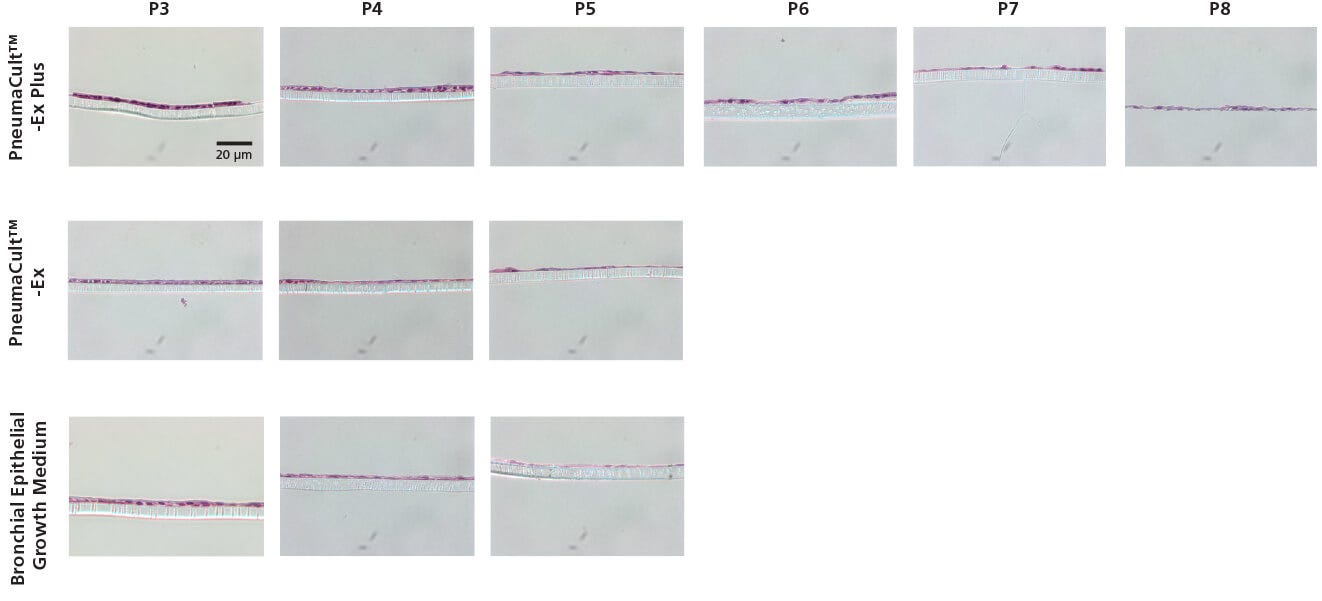
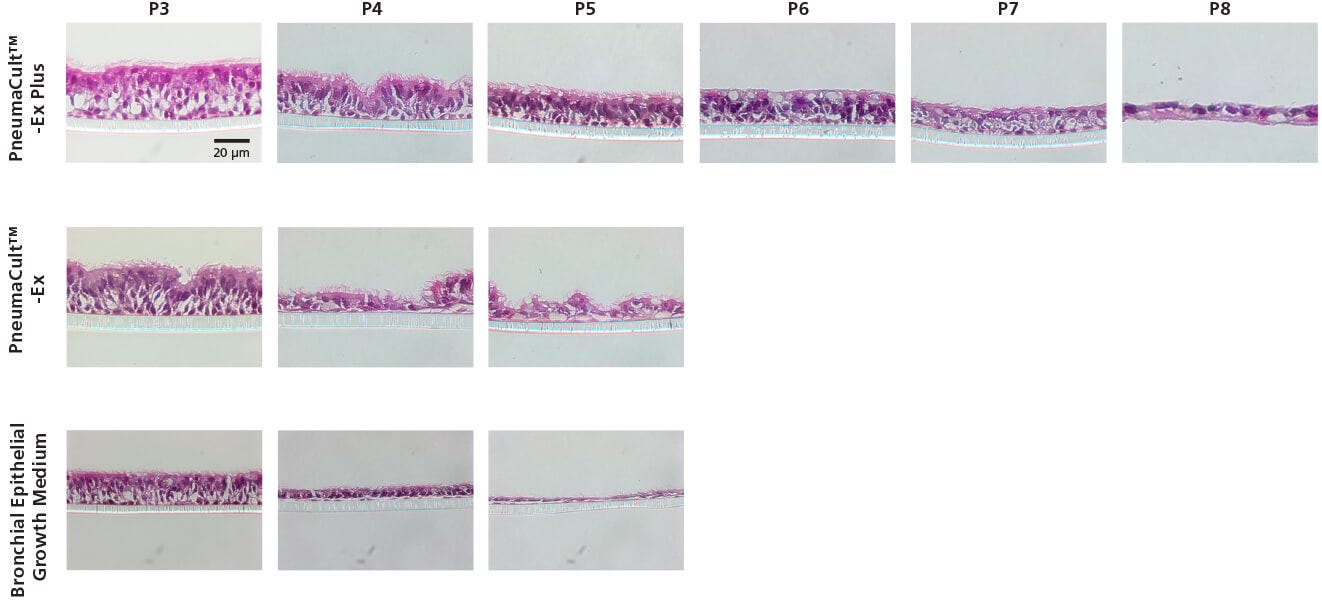
Figure 2. Representative Histological Cross Sections of ALI Cultures
P2 CF HBECs were expanded in PneumaCult™-Ex Plus, PneumaCult™-Ex, or Bronchial Epithelial Growth Medium, followed by ALI differentiation at each passage in PneumaCult™-ALI or Ultroser® G-based medium. After 28 days of differentiation, the ALI cultures were fixed, paraffin-embedded, sectioned, and stained with H&E. All images were taken using a 40X objective. Insert membrane was 10 µm in thickness. Ultroser® G-based medium was made based on a published formulation.5
PneumaCult™-ALI
Ultroser® G-Based Formulation
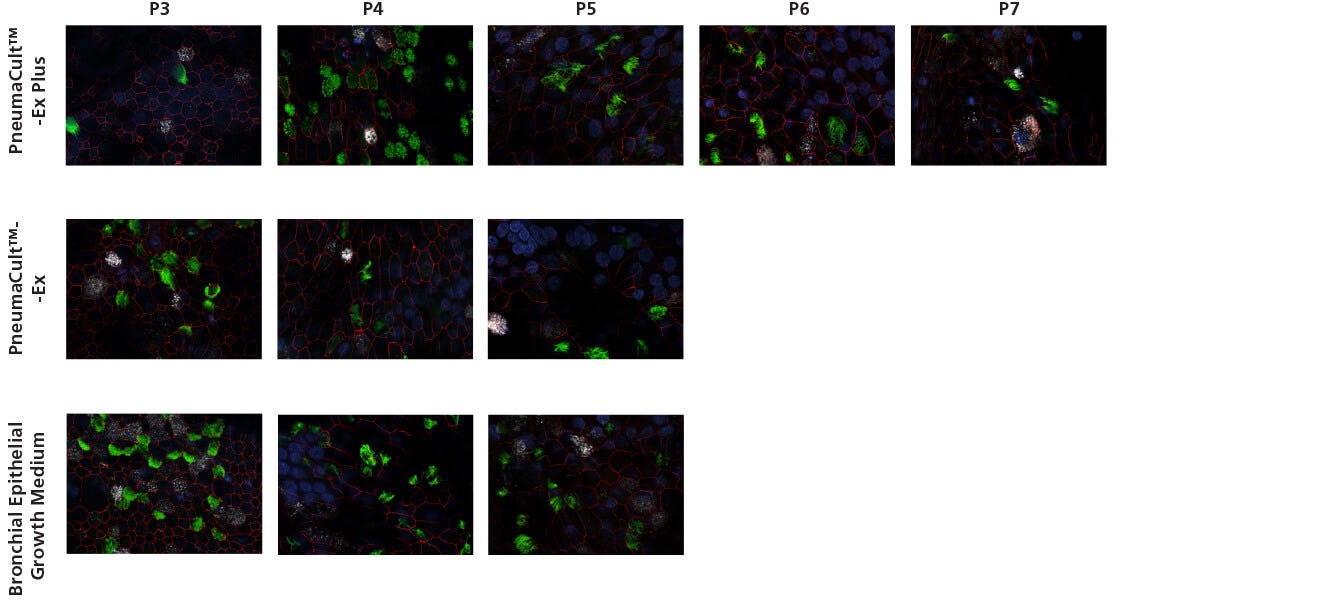
Figure 3. Representative Confocal Images of Whole Mount Immunostained ALI Cultures
P2 CF HBECs were expanded in PneumaCult™-Ex Plus, PneumaCult™-Ex, or Bronchial Epithelial Growth Medium, followed by ALI differentiation at each passage in PneumaCult™-ALI or Ultroser® G-based medium. After 28 days of differentiation, the ALI cultures were fixed and stained with antibodies for ciliated cells (AC-tubulin; green), Zo-1 (cell junction; red), and goblet cells (Muc5AC; white). The nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). All images were taken using a 63X objective. Ultroser® G-based medium was made based on a published formulation.5
PneumaCult™-ALI
Ultroser® G Based Formulation
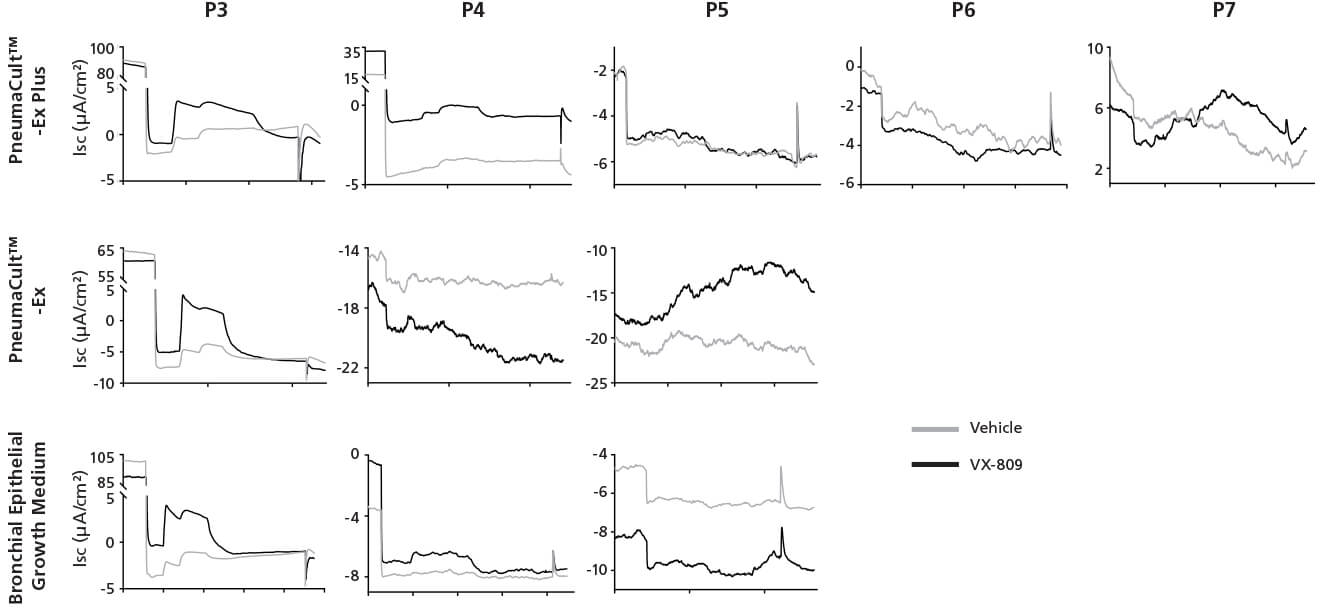
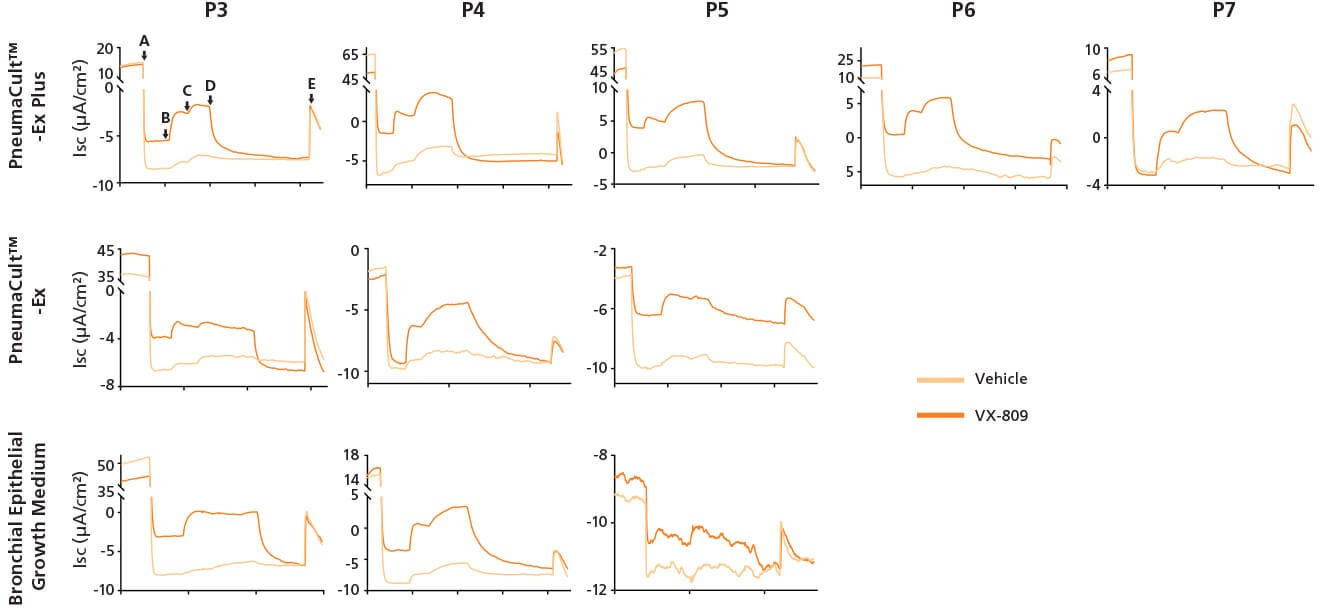
Figure 4. Representative Electrophysiological Characterization of ALI Cultures
P2 CF HBECs were expanded in PneumaCult™-Ex Plus, PneumaCult™-Ex, or Bronchial Epithelial Growth Medium, followed by ALI differentiation at each passage in PneumaCult™-ALI or Ultroser® G-based medium. After 28 days of differentiation, the ALI cultures were treated with either VX-809 or DMSO vehicle for 24 hours followed by Ussing Chamber assay. A: Amiloride, ENaC inhibitor. B: IBMX and Forskolin, CFTR activators. C: Genistein, CFTR potentiator. D: CFTRinh-172, CFTR inhibitor. E, UTP, Calcium activated chloride channels (CaCCs) activator. Ultroser® G-based medium was made based on a published formulation.5
Product Information
0.4 μm Pore Polyester Membrane Inserts
0.4 μm Pore Polyester Membrane Inserts
Explore These Resources
References
- Sosnay PR et al. (2013) Defining the disease liability of variants in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene. Nat Genet. (45): 1160–7
- Brodlie M, et al. (2015) Targeted therapies to improve CFTR function in cystic fibrosis. Genome Med. (7): 101
- Whitcutt MJ et al (1988) A biphasic chamber for maintaining polarity of differentiation of cultured respiratory tract epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 24(5): 420–8
- Gray TE et al. (1996) Mucociliary differentiation of serially passaged normal human tracheobronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 14(1): 104–12
- Neuberger T et al. (2011) Use of primary cultures of human bronchial epithelial cells isolated from cystic fibrosis patients for the pre-clinical testing of CFTR modulators. Methods Mol Biol. 741: 39–54
- Clancy JP et al. (2018) CFTR modulator theratyping: current status, gaps and future directions. J Cyst Fibros. Epub ahead of printing
- Goor FV et al. (2009) Rescue of CF airway epithelial cell function in vitro by a CFTR potentiator, VX-770. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 106 (44): 18825–30
- Gentzsch M et al. (2017) Pharmacological rescue of conditionally reprogrammed cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 56 (5): 568–74